Why are the two related? Because subclasses may need to know what specific class it is handling.
We get confused because we subclass generic interfaces to specify what type of items it is handling. For example, we may want to create a high level interface Renderer<T extends Shape> to draw shapes. Then we want to subclass it for:
SimpleRenderer<Point>: render points. The logical “relation” tree is:
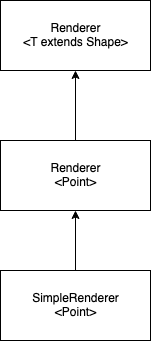
SimpleRenderer<ComplexShape>: render complex shapes. The relations are:

BufferedRenderer<LargeComplexShape>: render large complex shapes . We may think it would work to have:
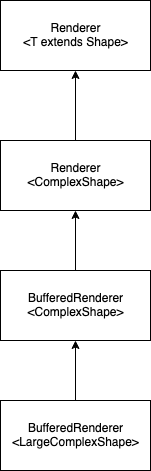
The purpose is to be able to have a single object manipulating both SimpleRenderer<ComplexShape> and BufferedRenderer<LargeComplexShape> “under” Renderer<ComplexShape>… but it does not work.
The relation tree for large complex shapes is actually:
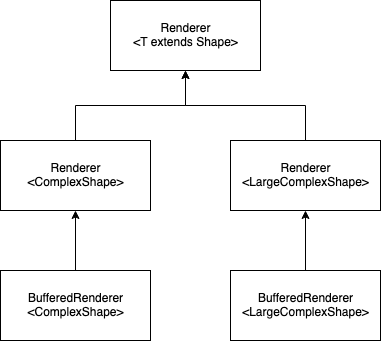
So we cannot use Renderer<ComplexShape> to manipulate both. Painful, isn’t it?
Here are my suggestions to help design classes:
Suggestion #1: do not think of Generics for inheritance, but to avoid casting object.
Suggestion #2: do I need to know the subclass type? if not, do not use Generics. Use interfaces